Docker is not a new term, this virtualization platform is popular for its ability to run applications in Containers. We can build and communicate containers with one another. Here we learn how to install the Docker CE platform on AlmaLinux 8 to create containerized virtual machines.
The key difference between normal virtual machines we run such as on VirtualBox is that in Docker not every container has to bring a complete operating system. For instance, you want to install and run Ubuntu 20.04 Server virtually but with a very minimalistic approach, I mean only core files that you need to run this server OS because, on Docker, the Containers are going to share the same kernel.
This makes us start multiple containers with different applications such as Apache web server, MySQL, etc. without asserting extra stress on the system hardware resources. Whereas in a normal Virtual Machine or hypervisor we install a complete Guest with the full-blown kernel that means, if we want to separate the web server from the database server, we would have to start two complete virtual machines including the operating system. In Docker, these are simply two independent containers that start the respective servers.
Out of the other benefits, one is the availability of Docker for all major operating systems- Windows, macOS, and Linux. Besides, we can easily pass the Docker containers on to teammates so that everyone pulls together and develops in the same environment. This distribution of the Docker containers takes place via the Docker Hub.
What will we learn here?
- Docker Installation process for AlmaLinux 8
- How to pull Images from Docker Hub to install and run a container?
- Commands to start, stop and restart Docker Engine
Steps to setup Docker on AlmaLinux 8
The steps given here will also work for RHEL and CentOS 8… Run the following commands:
1. Add Docker Repo on AlmaLinux
Add the official Docker CE repository on your AlmaLinux 8, so that we can install it without downloading its docker packages manually.
Note– It is a single command, thus use it as whole
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo2. Run system update
To let the system recognize the added Docker repository and the packages available in the same, run the system update that will force AlmaLinux to rebuild the system repo cache.
sudo dnf updateYou can check the added repo including others of your system using the command:
sudo dnf repolist -v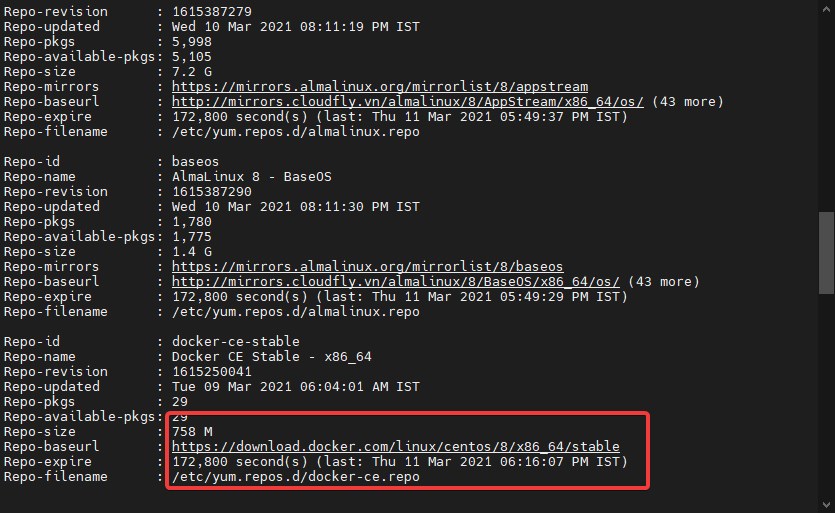
3. Install Docker CE Engine
So, we already have the Docker repo and now it’s time to run the simple command using the DNF package manager for installing the Docker-CE along with its command-line tool and containerd.io to efficiently manage the container lifecycle of its host system.
sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io4. Enable and Start Docker Service
Once the installation is completed, start the Docker service on your AlmaLinux and also enable it to run automatically with system boot.
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start dockerCheck the Status of the Service to know if it is working properly.
systemctl status docker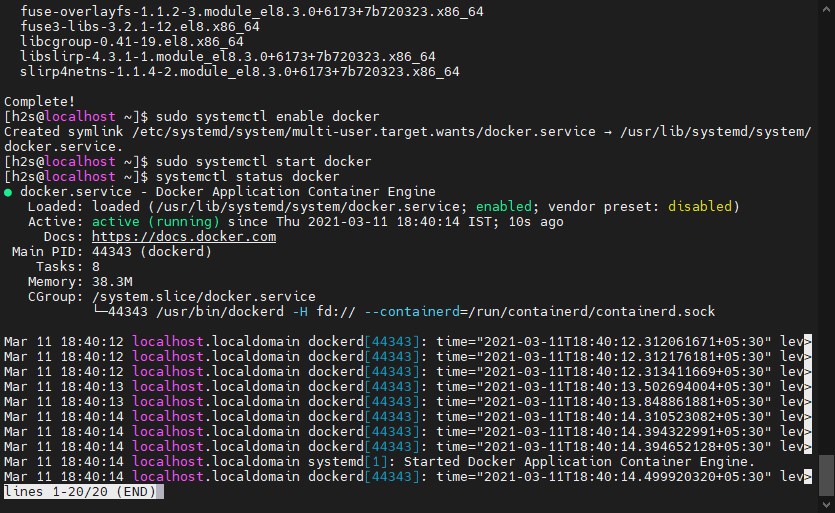
5. Add User to Docker User Group
To run docker commands we need sudo rights or root access and to avoid that add your current system user to the Docker group so that you can easily run its command for downloading and creating containers.
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERCheck whether your user is in the docker group or not.
id$USERIf you want to use some other user than the current one, simply replace $USER in the above command with the specific system’s user you want to give the rights to manage Docker.
Output:

Restart the Server
To make sure all the changes work smoothly restart your host AlmaLinux server or desktop where you have installed the Docker.
To get the information and details related to installer docker such as version, several containers installed, Host kernel version, Architecture, CPU, OS Name, etc. Type:
docker info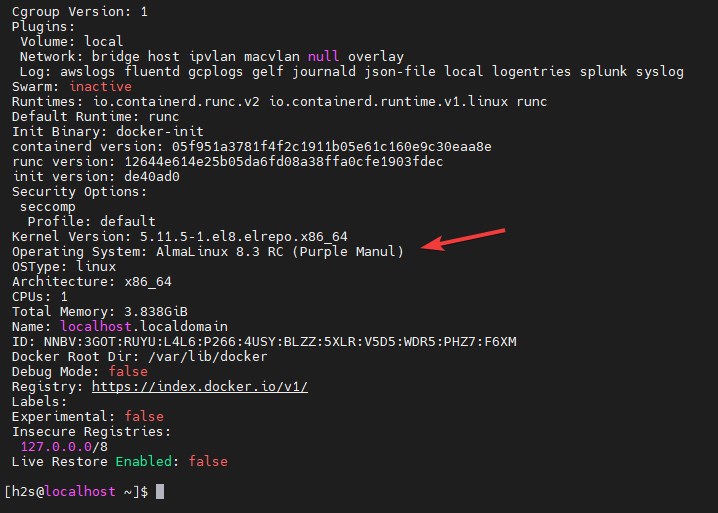
6. Test Docker run hello world
You can run Docker hello world image or download some distro images such as Ubuntu to create a Container and test, whether everything is working fine or not.
docker run hello-worldor
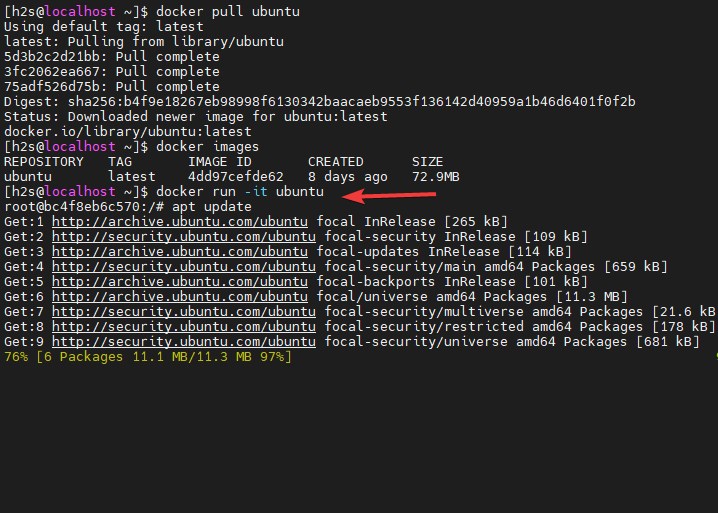
docker pull ubuntuThe above command will fetch the latest Image file of the LTS version i.e Ubuntu 20.04 LTS to install and create a container corresponding to it from Docker Hub.
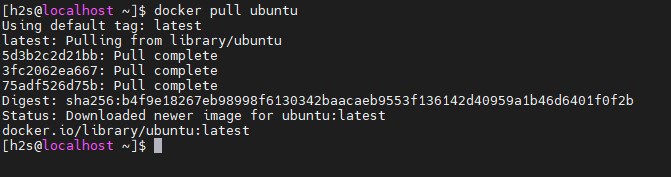
To know what are Images have been downloaded and available to use on your Docker system locally, run:
docker images7. Run Container
Now, we have the Docker Image of Ubuntu, let’s create and run a container using it. The command for that is very simple:
docker run -it ubuntuAfter that, you can use the Ubuntu APT package manager to run the command and install the various applications over it. Know more about its commands and work on the official documentation page.
Ending note:
Being a REHL-based operating system AlmaLinux works exactly like CentOS 8, thus the same commands and repositories to install for getting various packages including Docker can be used on it as well.

Great article, thanks. One small addition: I had to remove the already installed runc before: dnf remove runc