Modern technology is constantly evolving, and one exciting innovation is spatial computing. It has changed the we interact with the digital world. Although not entirely new, spatial computing has gained popularity due to wearables, mobile devices, GPS, and various apps. Let’s explore this cutting-edge technology and its impact on our digital experiences.
What is Spatial Computing?
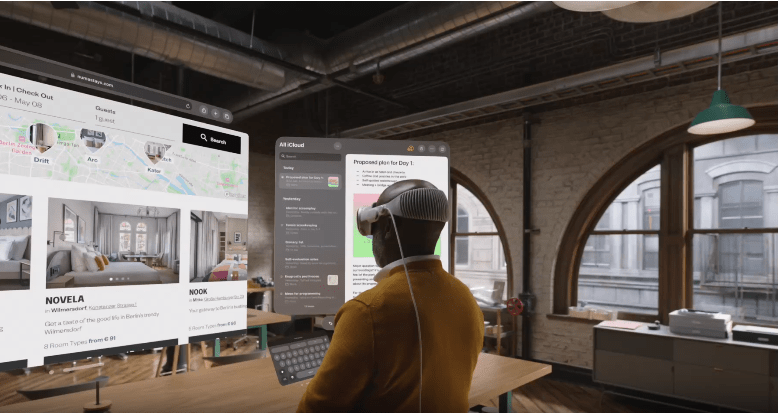
Spatial computing refers to the interaction between people and technology in a virtual space while eliminating the need for physical systems. It explores how individuals and technology seamlessly interact without being physically present. It operates within a 3D environment, utilizing digital technologies like virtual reality, extended reality, mixed reality, and augmented reality. In addition, the process involves the integration of computer vision, AI, and sensors to gather data, recognize objects, and understand languages.
Spatial computing integrates various immersive technologies seamlessly to create a virtual reality that immerses users in the digital environment. This means you can interact with the system without physical contact, experiencing the digital world through hand gestures and vision as if you were truly present in it.
The introduction of Apple’s Vision Pro headset has significantly propelled this technology, simplifying the integration of digital content with physical space and delivering a fresh and enhanced experience. Learn– Applications utilizing the idea of the Metaverse
How does Spatial Computing Work?
Spatial computing devices leverage data captured by cameras and sensors to create a map of the user’s surroundings. While advanced headsets like the Apple Vision Pro use multiple cameras, sensors, and specialized chips for mixed reality, smartphones may utilize their front-facing camera or a combination of cameras and LiDAR for spatial mapping.
The collected data is then processed by algorithms to recognize the shapes of objects in the user’s environment. More sophisticated devices might employ image recognition to classify the objects within the field of view. With a spatial map and understanding of the surroundings, these devices can overlay virtual objects that seamlessly blend with the physical environment. This opens up exciting possibilities, such as previewing furniture in your living room or witnessing virtual creatures racing through your hallway.
Benefits of Spatial Computing
- Better Creativity and Product Understanding
Spatial computing enables organizations to develop digital content for their products and services to promote better understanding among employees and enhance their work processes. This technology also opens up new creative possibilities for businesses to offer unique products or services that were previously beyond reach.
- Interactive Learning
Spatial computing has brought about a revolution in interactive learning by empowering students to interact with virtual environments and objects. This transformative approach has redefined the learning experience, offering real-time opportunities for students to explore and grasp scientific concepts. Through virtual reality (VR), students can actively engage in experiments and firsthand experiences, leading to a more captivating and impactful learning journey.
- Better Customer Experience
With spatial computing, organizations can enhance customer experiences by offering interactive and 360-degree previews of their products or services. Customers can virtually try out the products, gaining a comprehensive understanding of their appearance and functionality. For instance, spectacle manufacturers utilize augmented reality (AR) to enable users to try on frames, thereby facilitating better decision-making processes.
- Increased Productivity
Spatial computing empowers users with essential tools and information so that they can perform tasks with remarkable efficiency. Through its interactive features, users can complete tasks with higher accuracy and speed, resulting in a substantial increase in productivity. This enhanced efficiency translates to improved business operations, driving growth and success for organizations.
- Improved Safety
Spatial computing’s capabilities are revolutionizing brand services and product development by prioritizing safety. For instance, real-time information provided to car drivers through AR, MR, and other spatial computing elements helps avoid hazardous situations and potential mishaps. Car manufacturers are leveraging these technologies to create features that automatically prevent accidents, ensuring a safer driving experience for users.
Applications of Spatial Computing
Spatial computing possesses the potential to transform diverse industries by enabling experiences and applications that were once unimaginable.
Let’s explore some of the domains where spatial computing finds its applications.
- Learning and Education
Spatial computing offers an immersive and interactive learning experience that enhances knowledge retention and skill acquisition. Medical students can utilize spatial computing to practice surgical procedures in realistic virtual environments, while those in science and engineering can build and test virtual prototypes or conduct experiments.
Therefore, it can open the door for students to learn and get trained with new possibilities and revolutionize the way of grasping knowledge.
- Healthcare
Spatial computing opens up innovative avenues for diagnosing, treating, and monitoring patients. Doctors can utilize this technology to overlay virtual screens and diagnostic information onto the real world, aiding in making well-informed decisions. During surgeries, physicians could access a patient’s medical imaging scans through a headset, enhancing precision and accuracy.
Moreover, spatial computing can empower patients with physical or cognitive impairments by providing tailored virtual assistants and rehabilitation exercises, fostering their independence and well-being. This transformative technology has the potential to revolutionize healthcare practices, benefiting both medical professionals and patients alike.
- e-Commerce
Spatial computing can significantly enhance the e-commerce landscape. By leveraging AR, various applications now enable customers to virtually try on jewelry, apparel, spectacles, and other products. Moreover, some e-commerce platforms like IKEA have seamlessly integrated AR, allowing users to visualize certain products within their homes virtually. This level of interactive and immersive shopping has transformed the way customers make purchasing decisions, providing them with a more informed and satisfying shopping journey.
- Gaming and Entertainment
Spatial computing delivers captivating gaming and entertainment experiences by offering intuitive interactions with virtual objects and characters. Gone are the days of keyboards and joysticks; now, you can control avatars and manipulate game elements using hand gestures and gaze-based commands. This technology also redefines how you experience real-world events. With devices like the Apple Vision Pro, you can immerse yourself in an NBA game as if you were sitting court-side. Moreover, spatial computing allows you to preserve memories in a 3D spatial format, providing an extraordinary way to relive those moments in the future.
- Architecture and Design
Spatial computing empowers architects to design, visualize, and refine projects in the real world, eliminating the need for physical prototypes. This efficient approach saves time and costs while enabling iterative design processes. Similarly, designers can utilize spatial computing to craft virtual product prototypes and assess their functionality and ergonomics across various physical environments. This technology revolutionizes the design and testing phases, enhancing overall efficiency and creativity in the fields of architecture and product design.
Challenges of Spatial Computing
While Spatial Computing does come with several benefits, it also has certain limitations that we will discuss below:
- Privacy and Security Issues
Implementing spatial computing poses significant challenges in terms of privacy and security, mainly due to its reliance on real-time user data. Devices utilizing spatial computing technology gather vast amounts of information about user activities and surroundings. While many organizations adhere to stringent user policies, the potential risks of data exposure persist. Ensuring robust privacy and security measures becomes paramount to safeguarding user information in the realm of spatial computing.
- Huge Upfront Costs
The adoption of spatial computing presents a considerable challenge for many brands due to the substantial upfront costs involved. The specialized hardware and software required for its implementation can be quite expensive, making it inaccessible to many businesses. As a result, only a few large brands have been able to successfully integrate and deploy spatial computing into their infrastructure so far. The significant financial investment acts as a limiting factor, preventing widespread adoption across various industries.
- Low Acceptance Rate
Currently, the acceptance rate of spatial computing remains relatively low, mainly due to its novelty as a technology. While it is now being used in various industries, a significant portion of users is still unfamiliar with its potential and how to leverage its benefits effectively. Additionally, spatial computing is currently limited to specific products and applications, which hinders its widespread popularity and adoption. As technology continues to evolve and gain recognition, its acceptance rate is expected to increase over time.
Wrapping Up!
Spatial computing is the emerging frontier that is revolutionizing user interactions with digital devices across diverse industries. This amalgamation of various technologies has opened up a multitude of possibilities, captivating organizations seeking to leverage its immense potential for enhancing user experiences.
Prominent companies such as Google, Apple, and Microsoft have already embraced spatial computing on a significant scale and are continually striving to enhance their capabilities. While it still has a journey ahead, the future looks promising, as more and more players in the industry are expected to embrace spatial computing, making it a ubiquitous technology in the not-so-distant future.
Related Posts
What is a juice-jacking attack? How can we be safe from such attacks?
Getting the right dashcam for your needs. All that you need to know
WhatsApp iPad App Gets Major Overhaul, Adds New Communities Feature
Moto G85 5G launched in India but is unlikely to beat VIVO or XIAOMI
Rise of deepfake technology. How is it impacting society?
Smartphone Apps Get Smarter- Meta AI’s Integration Across Popular Platforms