If you want to know how to open and use the command prompt app in Windows 10, 7, or 8 but using different ways including keyboard shortcuts then go through the methods given in this article…
In Windows 10, 7, or other previous versions, most of us use the mouse & GUI interface to navigate and perform various tasks. However, there are certain cases where we have to use command line commands in the command prompt (CMD). Even if the CMD does not seem particularly attractive, it is a very quick way to perform various tasks such as maintenance, analysis, enabling various services, and updating the Windows system.
What is the command prompt?
The command prompt (also console or terminal) is a program in Windows operating system, a text-based user interface, to run various commands for system control and management. It comes with a GUI interface to easily allow users to execute commands, manage the PC and solve problems.
When there was no GUI implementation in the older operating system of Microsoft that is MS-DOS, it was completely based on the command line to operate and manage the system.
Well, we can do the same, because that interface is now available in the form of a Command terminal to pass certain predefined CMD commands to the operating system.
Multiple ways to open the Windows 10 command prompt
The answer to the common question “Where can I find the command prompt?” Well, as we know command prompt is also an app like any other software available on Windows, thus we can run CMD quickly. There are several ways to open the command prompt in Windows 10 (and Windows 8) and here are the best possible ones…
1. Bring up the command prompt with the keyboard
Many times you would want to have a keyboard shortcut to open a command prompt on Windows just like we do for the terminal in Ubuntu Linux. Well, that is possible, however, you have to set that manually and here I will let you know how?
- Simply in the Windows 10 search box type- CMD and select Open file location.
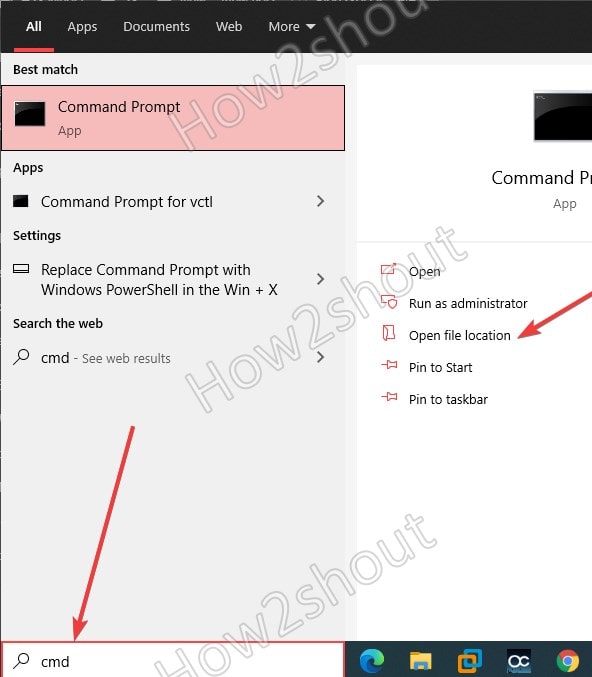
- Now, right-click on the Command prompt shortcut icon and select properties.
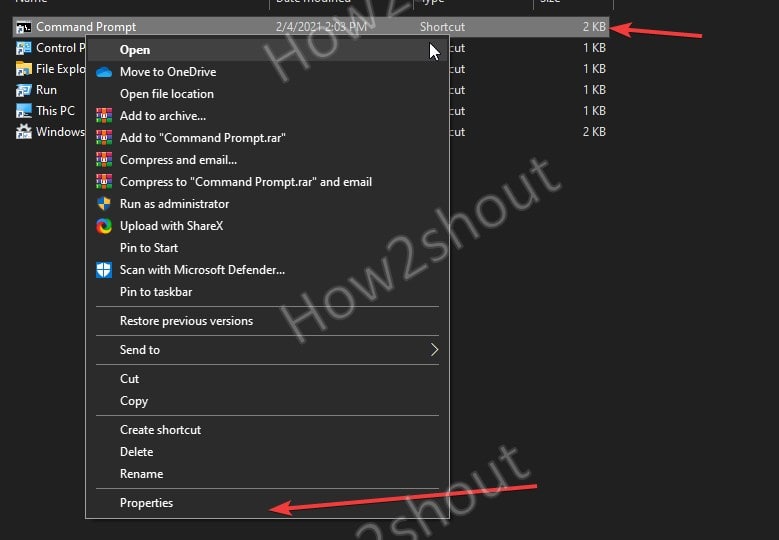
- Go to the Shortcut column and press any keyboard key to automatically set the shortcut that you want to use to open CMD every time.
- For example, here I am setting it to Ctrl+Alt+C
- Hit the Apply button to save the same.
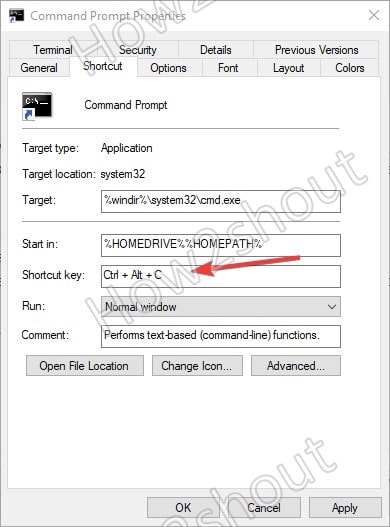
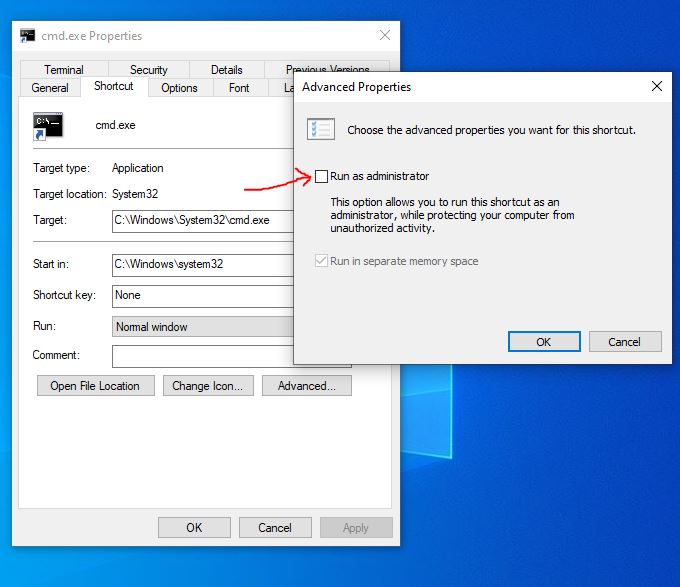
- In case you want to start the command prompt using the keyboard but with administrative rights. Then select the Advanced button and check the box given for the same.
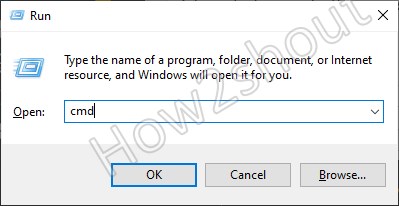
2. Open Command prompt using Run box
The second method is also simple and quick. In all Windows versions, we have a tool called Command run box. Where we can type pre-defined commands to open various applications including CMD.
Thus, press the Win+R key on your keyboard and type CMD then hit the Enter key. If you want to open in Administrative mode, then press the Shift button and then hit the Enter Key.
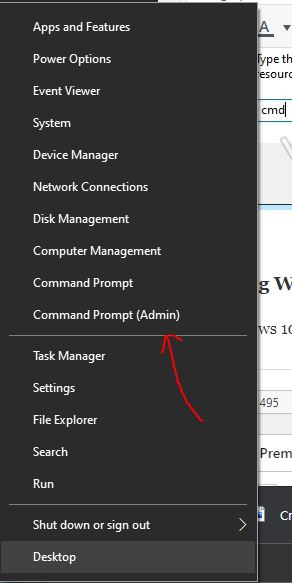
In Windows 10, when you right-click on the Start button, a pop-up menu will open with various options and shortcuts to open apps and settings. However, in the latest versions of Windows, you will not get the Command prompt option there because it has been replaced by Powershell by default. To bring that back, simply in the search box type Settings ⇒ Personalization ⇒ Taskbar and turn off the Toggle button given for “Replace Command prompt with the menu...”.
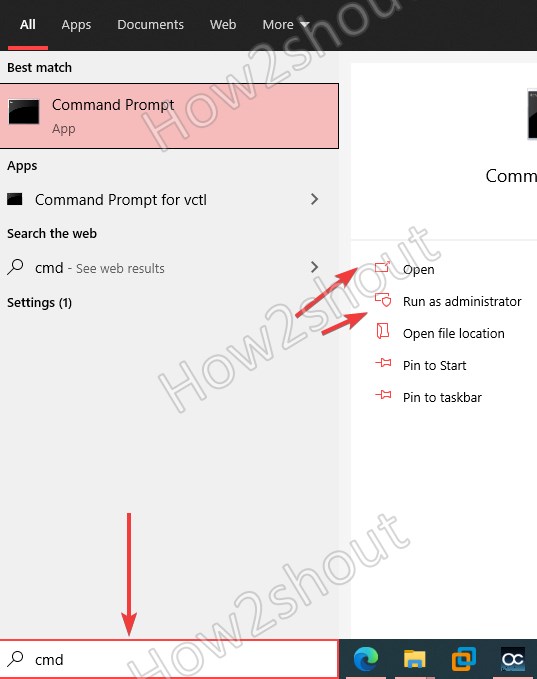
4. Run Command prompt from Search results
This one is the most common and maybe you already have been using it. In this method, we just need to type either command prompt or CMD in the Windows 10 Search box. The system will give the results, then click on the icon to Open or for running CMD with Administrative rights, use the option available for it.
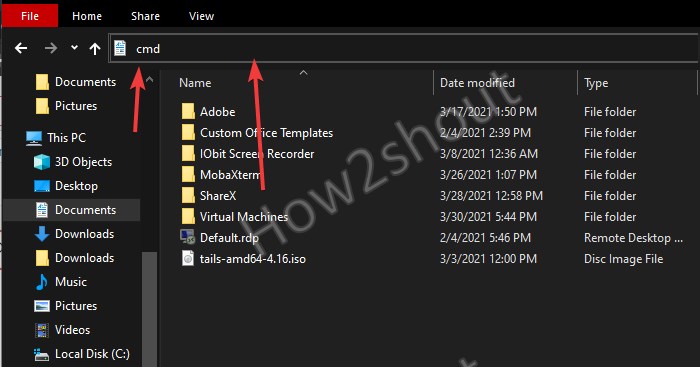
5. Start Command prompt from File Explorer Address Bar
While working inside some folder or anywhere on Windows using its File Explorer, the easiest way to open CMD is using the Address bar using mouse and keyboard.
Click on the Address bar or press Alt+D, type CMD, and hit the Enter key.
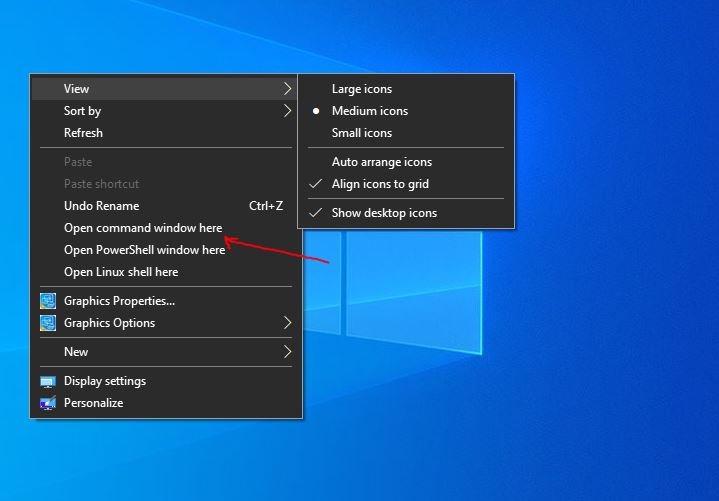
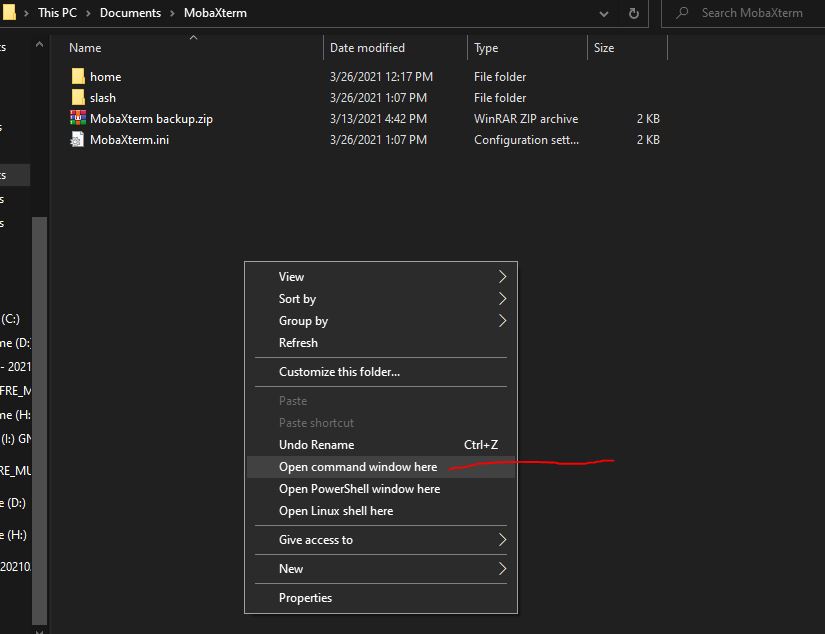
6. “Open Command Prompt Windows here”, in Context Menu
Well, if you have enabled the Command prompt to appear in the Windows Context menu then we can start CMD directly with just one right-click, anywhere. Press the shift key and right-click anywhere on your desktop screen.
Alternatively, you can also open the CMD anywhere in your current directory by just pressing shift and right-clicking.
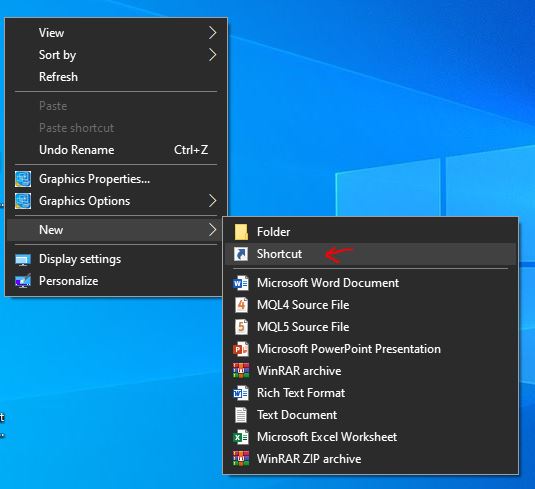
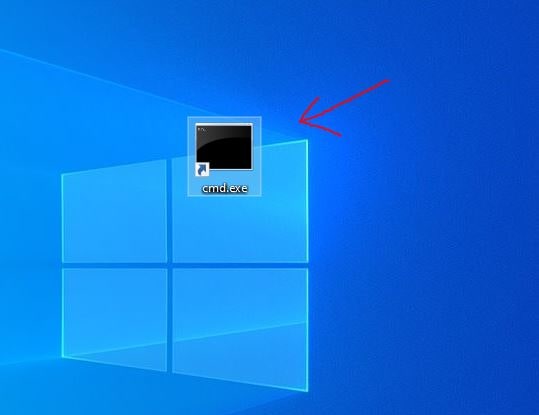
7. Create CMD Desktop Shortcut
To create a Desktop shortcut for Command Prompt on Windows 10 or in the previous version, right-click anywhere on Desktop’s space and select New ⇒ Shortcut.
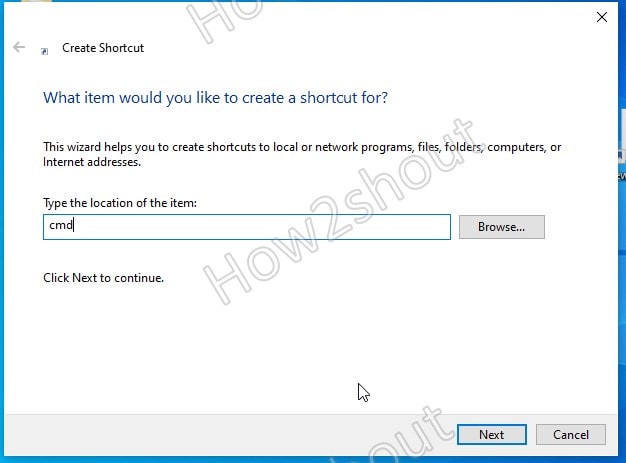
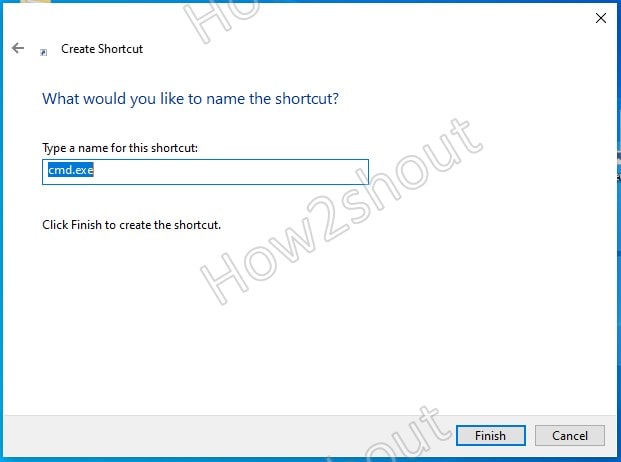
Type CMD in the “Type the location of the item” box and click on the Next button.
Press the Finish button to finally create the shortcut.
If you want to run it every time with Admin rights, then right-click on the created shortcut, select properties, click on the Advanced button, and check the box given for “Run as Administrator“.
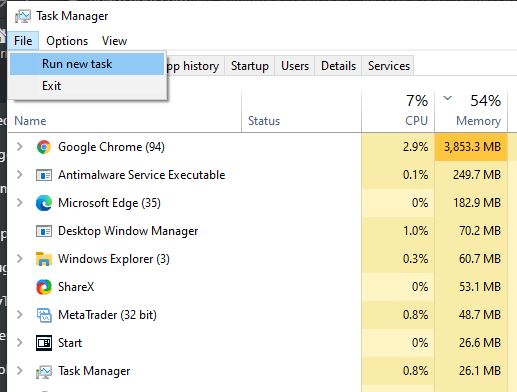
8. Start from Windows Task Manager
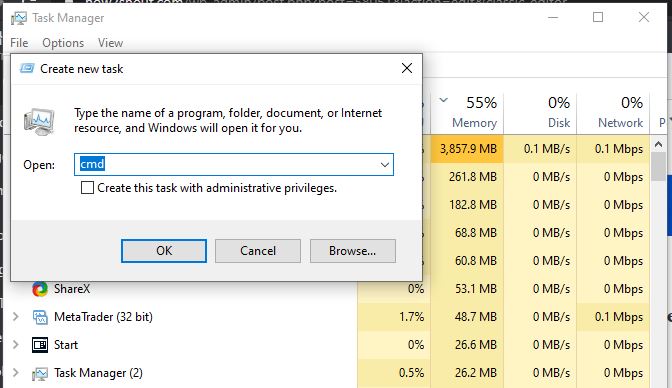
This method is similar to the one we used to start the Command prompt using the Run command box. In the same way, if you are on Windows 10 or 7 Task Manager, then click on File ⇒ Run New Task. Type CMD and hit the Enter button you will get the CMD command line with Admin rights…
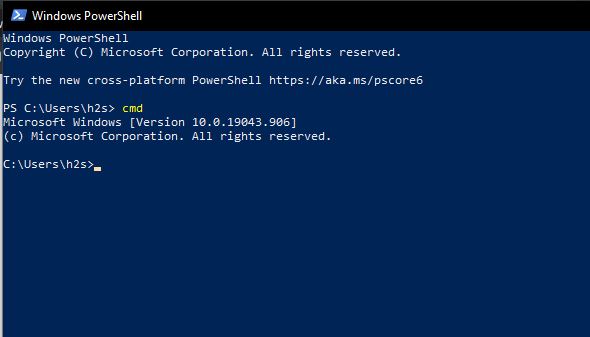
9. Use Prompt in Powershell shell
If you already using Powershell for some task, then without leaving your current session, it is possible to switch to Command prompt. For that simply type- CMD.
So, these were few shortcuts and quick ways to open a Command prompt on Windows 10, 8, and a few also applicable for Windows 7. However, if you have some confusion between CMD and Powershell, then let’s discuss a little bit as well.
Command Prompt vs. Windows PowerShell: What’s the Difference Explained?
Initially, the Windows operating systems have only one tool to issue commands to manage various services and system activities including apps. However, later with Windows 7, Microsoft introduced one more command-line tool called PowerShell which is now popular among developers/administrators and also available to install for Linux operating systems. You can see this article to learn about that- How to install Powershell on Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, and other Linux distros using SNAP.
Basically, PowerShell is the updated version of the command prompt. Yet, what is the difference between the two tools?
CMD is commonly used by standard and system administrators to process batch files, troubleshoot common errors, and repair or manage system files. Whereas Powershell offers new sets of powerful tools, of course, that also makes it more complex than CMD.
Actually, the Command prompt was not able to keep up with the shell that Linux users and administrators are used to. Therefore, to remove that gap Microsoft introduced PowerShell for Admins to perform various tasks, for example using Powershell we can control and edit an entire network and all of the systems in it.
It is a complete scripting environment that can be used to create complex scripts for managing Windows systems.
In contrast to CMD, which can only execute batch commands, PowerShell also offers the option of using batch and PowerShell commands. In addition to .exe, .cmd, .msc and .vbs, PowerShell also loads other user files such as .docx, .jpg, .xls, and .pdf.
In fact, we can use the commands of the Command prompt in Powershell, but the reverse is not possible. They both are closely linked, that’s why we can directly call CMD during a PowerShell session by entering the “CMD” command.
Few Important CMD commands
We already have talked about the way to access CMD on Windows 10/8/7, now here are some common commands that we can use to start learning and getting familiar with the working of command prompt.
| dir | Lists a directory content |
| cd .. | Changes to the higher directory |
| cd <name> | Changes to the directory with the name entered |
| cd \ | Change to the root directory |
| copy / xcopy | Allows files to be copied |
| exit | Exits the command prompt |
| move | Moves a file to another location |
| cls | Clears the contents of the command prompt |
| md | Creates a new directory |
| approx | Deletes a directory |
| comp | Compare data content |
| compact | Compression of files |
| copy / xcopy | Copy files |
| erase / del | Delete one or more files |
| expand | Unzip the file |
| fc | Compare files |
| mkdir | Create directory |
| move | Move files |
| rename | Rename files |
| replace | Replace files |
| rmdir / rd | Delete directory |
| tree | Display folder structure graphically |
| type | Display the content of text files |
| chkntfs | Change disk verification |
| defrag | Defragment the disk |
| diskpart | Disk management |
| driverquery | Show installed devices |
| format | Format data carrier |
| label | Change the volume label |
| Fashion | Configure devices |
| mountvol | Assign or delete a drive letter |
| verify | Monitoring of a data carrier |
| vol | Display the name of the hard disk |
| shutdown-l | the user will be logged off. |
| shutdown-r | Restart your PC |
| ipconfig | you can see your IP address. |
| tasklist | list of all active processes |
| rmdir | Rename Folder |
| mkdir | Create folder or directory |
| help | To see a list of all CMD commands |

Related Posts
How to Install 7-Zip on Windows 11 or 10 with Single Command
Install Google Earth on Windows 11 or 10 Using a Single Command
How to install Gaming Services on Windows 11
How to Install Telnet Client on Windows 11 Using PowerShell
How to Install ASK CLI on Windows 11 or 10
How do you install FlutterFire CLI on Windows 11 or 10?