Installation Docker on CentOS 8 Linux / Stream or RHEL 8 is simple and same as before we were doing on CentOS 7.5. Docker is available in two editions community and enterprises. Here we let you know to install Docker community edition which includes Docker Engine, Docker Command line and Docker Compose.
So, let’s get started with the tutorial:
Step 1: Open Command Terminal and login as root.
For that simply type:
su
And when it asks for the root password given that.
Step 2: Install some required packages for the Docker installation
Device-mapper-persistent-data and lvm2 are required by the device-mapper storage driver, while yum-utils provides yum-config-manager to set repository using a single command.
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
Step 3: Add Docker repository to CentSO 8 or RHEL 8
To download and install the Docker’s latest version of the CentOS 8 or Stream, we will use the Yum config manager to configure the Docker repo, so that our system can recognize the location from where to fetch the RMP packages.
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
or
dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Step 4: Run System update command
After enabling the Docker repo, run the system update command to flush the cache. For that type:
dnf update
or
yum update
Step 5: Command to instal Docker community edition on CentOS 8
Finally, everything has been set up and its time to install Docker engine on our server with CLI and Compose components.
yum install docker-ce
or
dnf install docker-ce
In the case above command give an error:
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io Last metadata expiration check: 0:00:50 ago on Wed 02 Oct 2019 08:09:04 AM EDT. Error: Problem: package docker-ce-3:19.03.2-3.el7.x86_64 requires containerd.io >= 1.2.2-3, but none of the providers can be installed - cannot install the best candidate for the job - package containerd.io-1.2.2-3.3.el7.x86_64 is excluded - package containerd.io-1.2.2-3.el7.x86_64 is excluded - package containerd.io-1.2.4-3.1.el7.x86_64 is excluded - package containerd.io-1.2.5-3.1.el7.x86_64 is excluded - package containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64 is excluded (try to add '--skip-broken' to skip uninstallable packages or '--nobest' to use not only best candidate packages)
So, we are getting an error because the dnf trying to find the latest upgrade packages even if the dependencies do not support it. Thus we use –nobest flag to cure this problem.
Thus the command will be
dnf install --nobest docker-ce
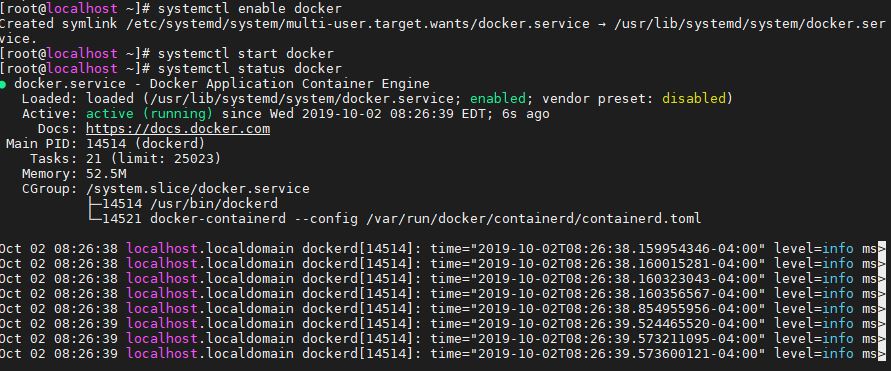
Step 6: Enable Docker System Service (daemon)
Here is the command to make the Docker service as a system so that it can start automatically with system boot up.
systemctl enable docker
Step 7: Start Docker service
Now, finally, we start the docker service to start working around with it.
systemctl start docker
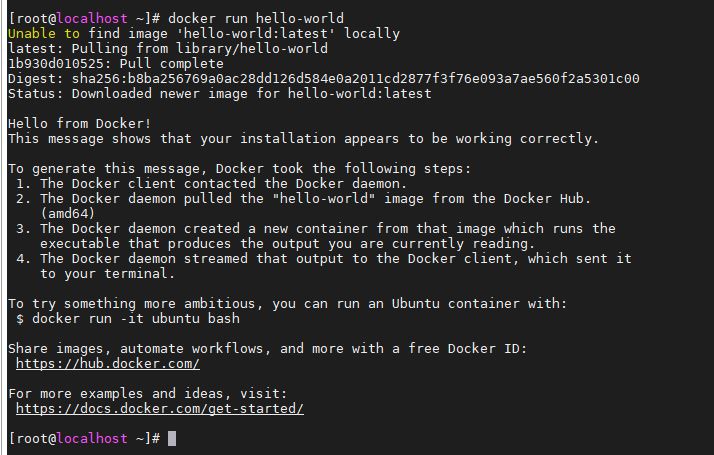
Step 8: Verify that Docker Engine working perfectly
Let’s fetch the hello-world image to test the Docker working. However, we directly command the Docker to run hello-world image which it will not find on our local system and pull automatically from the Docker hub.
docker run hello-word
Step 9: Pull some Linux distro image
Just to give you an idea, how we can run different Linux operating system on CentOS 8 installed Docker. Hence, here we will pull the latest Ubuntu image. For that, the command is
docker pull ubuntu
By default it uses the latest tag, means it fetches the latest stable version of the Ubuntu.
After downloading it run to use the Ubuntu on CentOS 8 virtually using Docker
docker run -it ubuntu
For more images, you can visit Docker Hub

Related Posts
How to create email groups in Gmail? Send one email to multiple recipients in a matter of seconds.
Getting the right dashcam for your needs. All that you need to know
How to Install 7-Zip on Windows 11 or 10 with Single Command
How to Install ASK CLI on Windows 11 or 10
How do you install FlutterFire CLI on Windows 11 or 10?
How to create QR codes on Google Sheets for URLs or any other text elements