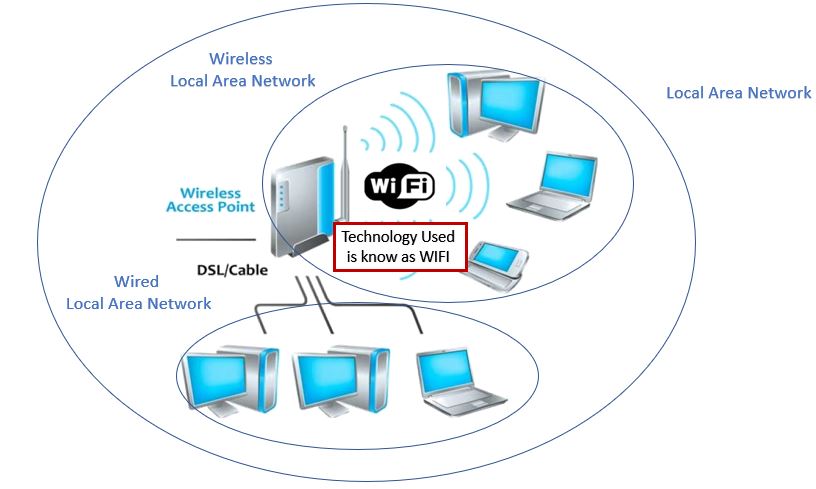
Let’s start with a literal introduction to WLAN and WiFi. WLAN is an acronym for Wireless Local Area Network. It refers to the application of wireless communication technology to interconnect computer devices to form a network system that can communicate with each other and share resources. For example, multiple computers or devices connected with each other using the Wireless network of a wireless router to provide local connectivity. These computers or laptops installed with the wireless adapter or Wireless LAN card can communicate with each other for files transfer, printer sharing and more locally; the internet connection is not compulsory.
WLAN uses ISM (Industrial, Scientific, Medical) radio broadcast band communications. The WLAN 802.11a standard uses the 5 GHz band, and the maximum supported speed is 54 Mbps, while the 802.11b and 802.11g standards use the 2.4 GHz band, which supports speeds of 11 Mbps and 54 Mbps, respectively. The current WLAN includes the following protocol standards: IEEE802.11b, IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11g, IEEE802.11E, IEEE802.11i, and WAP, however, in 2009 IEEE802.11n was added for better connectivity; it operates in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands at a maximum data transfer rate of 600 Mbit/s. For more info about the WiFi protocols or history refer to the Wikipedia.
On the other hand, the WIFI is a trademark of WLANA (Wireless Local Area Network Alliance) or WiFi-Alliance. This is trademark only guarantees that products using the trademark can cooperate with each other. It is actually not related to the standard itself. However, because WIFI mainly uses the 802.11b protocol, people gradually become accustomed to it. Use WIFI to call the 802.11b protocol. From the perspective of inclusion, WIFI is a standard of WLAN. WIFI is included in WLAN and belongs to a new technology adopted in WLAN protocol. The WiFi coverage is up to 300 feet (90 meters)
WIFI (Wireless Fidelity) technology as we told, is a brand of wireless network communication technology based on the IEEE 802.11 series of standards. The purpose is to improve the interoperability between wireless network products based on the IEEE 802.11 standard, and the Wi-Fi Alliance. (Wi-Fi Alliance) holds, in short, WIFI is a kind of wireless networking technology. In the past, it was connected to a computer via a network, and now it is connected via radio waves. The Wi-Fi Alliance (also known as: Wireless Local Area Network Standardization Organization WECA) was founded in 1999, when the name was called WirelessEthernetCompatibilityAlliance (WECA), in October 2002, officially changed its name to Wi-FiAlliance.
Like Bluetooth technology, WiFi is a short-range wireless technology used in offices and homes. The technology uses a frequency band between 2.4 GHz to 5GHZ based on the 802.11 standards, namely IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11b, IEEE802.11g, dual-band and so on. When the signal is weak or interfered, the bandwidth can be adjusted to 5.5Mbps, 2Mbps, and 1Mbps, and the bandwidth can be adjusted automatically, which effectively guarantees the stability and reliability of the network. This technology has its own advantages, so it is favored by manufacturers.
The WiFi used in numerous devices such tablets, smartphones, Smart TVs, Video game consols, home network and other consumer electronics. So, any product that has posses the WiFi tech and approved as “Wi-Fi Certified” are certified as interoperable can communicate with each other. For example, mobile device and Smart Tv both can communicate with each other and share the data on Wireless nertwork or technolgy know as WiFi.
Related Posts
From Wi-Fi to Li-Fi: A Glimpse into the Future of Wireless Technology
What is the difference between a WiFi and an Ethernet connection?
Tips to Secure and Encrypt your WIFI Network Security
How to Fix Automatic Airplane Mode on and off in Windows 10 Pc or Laptop
All that you need to know about Wi-Fi calling or VoWiFi service
Wi-Fi 6 standard benefits and the way it will improve wireless connections