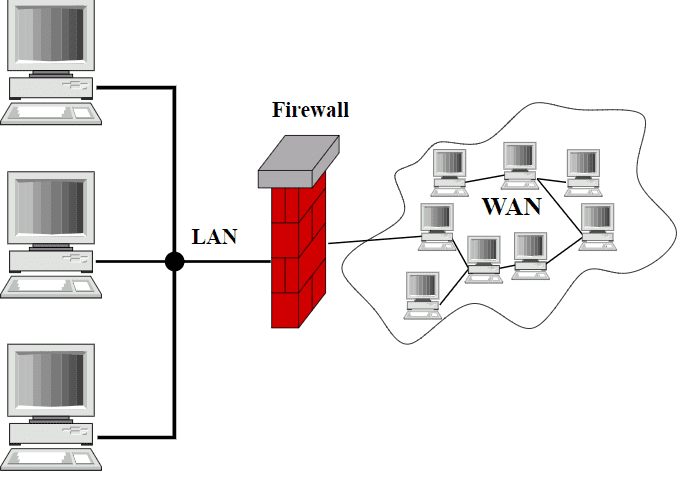
A firewall- as the name indicates- is a Fire like Wall that protects your network from unwanted intruders. Firewalls play a crucial role in the field of network security. These are devices that can be specified as hardware, software, or a mixture of both. It acts as a barrier to the outside threats and works on a predefined set of rules known as the Access Control List, by monitoring and controlling the incoming and outgoing traffic. It decides which traffic should get through and which one should be denied. A firewall is like a boundary or security personnel at the entrance who works for the safety of a system.
Well, there are three basic types of Packet Filters, Stateful Inspection and Proxy Server Firewalls, however, we gone one step ahead and tried to explain five types:
Firewall Category
1. Host-based Firewalls
These firewalls are located inside your system. For example, You can find the firewall setting under the control panel option if you are using Windows operating system. It’s actually software that is working inside your machine to protect it from untrusted sources.
Location: Go to Control Panel> System and Security > Windows Firewall
You can find several options there:
- Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall
- Change notification settings
- Turn Windows Firewall on or off
- Restore defaults
The antivirus software installed in your system also manages the settings of a firewall which can help prevent hackers or malicious software from gaining access to your PC through the internet or a network.
2. Network-based Firewalls:
These firewalls are generally used in the form of hardware in large organizations to scrutinize the entire network and safeguard the company’s essential information. A host-based firewall is a part of your system software package but in the case of a network-based firewall, it is dedicated hardware that runs firewall software that solely works to protect data. Although it is not mandatory to have dedicated hardware as you can install it at any server you want but for better performance, the dedicated ones are recommended.
Every organization has an internal network which can also be called a trusted network, which is used by authenticated personnel of the company. Then, there is an external network known as the World Wide Web or Internet which is public and full of threats, therefore is referred to as the untrusted network. A company’s firewall checks every data packet which tries to enter the company’s internal network or log in to the private server and prevents it from harming the organization’s internal server.
What is a Data Packet?
Whenever we download any file from the internet it does not get downloaded altogether. The file is divided into smaller packets that arrive at our system one by one in a particular sequence. Some of these packets contain the information about the sender and receiver’s IP address along with the actual data that we wanted to download known as the payload.
5 Types of Firewall
1. Packet Filtering Firewall:
There are seven layers in the networking architecture or OSI (Open System Interconnection) model which are as follows (from bottom to top):
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
Packet filtering firewall is also known as Layer 4 firewall. It is a better performing firewall as it works on the Network and Transport layer.
- It basically checks the IP (Internet Protocol) header and TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) header in the packets passing through the network. In the IP header, it mainly checks the sender and receiver’s IP addresses and in the TCP header, it mainly checks the Port number.
- Port numbers are some digits written after the IP address is separated with a colon, for ex: 212.321.1.1:8080. Here 8080 is the port number. These are crucial for successful data packet transfer.
- This firewall is capable of blocking malicious IP addresses and if we don’t want any packets to arrive from that particular network, it can even block the suspicious network completely.
- It can also block a service, like HTTP, FTP, etc.
- Its “Default allow policy” allows everything to get through apart from the ones mentioned in the table of predefined rules known as Access Control List. This table contains a set of rules including the Source IP (Ex: 162.42.0.0 for an entire network) and Source Port (Ex: 8080 for http) of the network or IP address to be blocked and the Destination IP and Destination port of the network that needs to be secured from external access.
2. Application (Proxy) Firewall:
- It is an advanced firewall that has the capability to scan up to the Application layer.
- The proxy firewall scans the data along with the header, to check the points that may contain malicious information. Whenever you tend to use a web service or try to log in with your username and password, your data passes in an encrypted format through the HTTPS protocol which is an http facility with a secure socket layer. Your request first goes to the network firewall which simply checks the IP address and if the request is appropriate according to the set of predefined rules, it transfers the request to the next stage i.e. Proxy firewall.
- Proxy firewall verifies the data (username and password) and then forwards it to the web application/ database/ main server if it’s justified and genuine. But if the data is invalid, the request is rejected immediately. On being valid, it gets a secure session in which it can avail of the service it was requesting for.
- For example, Gmail puts some specific emails under the spam section based on certain keywords which seem to be irrelevant or have an improper sequence of data packets while scrutinizing the incoming traffic thoroughly.
A proxy firewall does not let the internet know which computer actually wants to visit the website. It hides the system from hackers on the internet. It does not disclose the identity of the origin thus protecting the system from potential malware.
3. Circuit level gateway:
- A circuit-level gateway is a type of firewall that provides session-level control over network traffic. Similar in operation to packet filtering routers, this gateway operates on a higher level of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model protocol stack.
- Circuit level gateways are host-based and reside on individual clients and servers inside the network rather than on a dedicated machine as they do with other types of firewalls.
- Circuit-level gateways examine incoming internet protocol packets of the session-level TCP or UDP by handing off incoming packets to other hosts.
- These are rarely used as a standalone firewall solution, instead, they are typically used in combination with Application layer proxy servers and packet filtering features in dedicated firewall applications.
4. Stateful inspection firewall:
The stateful multilayer inspection firewall is yet another revolution of the previous models discussed above and in fact, it would normally combine aspects of the previous three models i.e. packet filtering, circuit-level gateway, and application-level gateway.
- As inspections happen at multiple layers of the communication, it works on the whole OSI stack.
- This firewall has the ability to go all the way from the lower level TCP packets up to the actual application communication protocols. This type of firewall can do all kinds of work that we have read about so far.
- It can inspect the content of http requests but because it is stateful, it can also work across packets and requests and do things like only allowing packets from non-active connections that require a greater level of awareness than just looking at individual packets.
- Rather than treating every single network packet individually as a stateless firewall, it can take a stateful approach and actually look at these packets more holistically.
- The stateful multilayer inspection firewall can start making filtering decisions based on cumulative data. Data that contains not just the information which is flowing through the individual packet but how these packets fit in this broader concept which is a connection with requests and responses.
5. Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW):
Depending on the nature and size of a business, IT departments use different types of Next-Generation Firewalls to operate.
- A Next-Generation Firewall allows better control and better visibility into all organizational activities and protects organizations from potential cyber-attacks and data thefts.
- A traditional firewall will protect the data entry and exit points, however, many transactions happen between these two points which are equally prone to threats. With NGFW, you can set up controls at every point and establish complete control over data coming in and out and on devices that are transmitting data.
- NGFW also provides a holistic view of the network including analytics on network traffic.
- It also enables organizations to run operations smoothly by preventing persistent malware attacks.
If any organization wants to ensure that it has the right NGFW, here are few tips to consider:
- Whenever an organization sets up a relationship with a vendor, it should ensure it to be a strong and strategic one. If the vendor can understand the firm’s infrastructure, he should be able to map the infrastructure with an NGFW solution.
- While implementing an NGFW, make sure it automates regular and routine tasks such as Impact assessment, User Identification, and Policy tuning.
- NGFW should align with the company’s ecosystem and any third-party solutions that are used by the company.
- It is imperative to adapt quickly as network threats are increasing day by day.
Which Firewall will be best suited for which environment?
- As the Packet filtering firewall only checks the header and not the payload, it does provide a low level of security. Therefore, these will be best for a Low-Risk Environment like a local vendor shop.
- Application firewalls take more time in filtering the requests as it checks the header as well as the actual data inside a packet. Therefore, they provide a better level of security as compared to Packet filtering firewalls and can be used in a Medium risk environment such as colleges and universities.
- The stateful multilayer inspection firewall and NGFW provide the best level of security and they can be implemented in High-Risk Environments namely a hospital server that contains important information of patients and staff members.
One can choose a firewall as per the need of their environment.
Related Posts
What is Identity Theft? All that you should know about this form of cybercrime
How to install BetterCap on Windows 11 or 10
Guardians of Data: How Role-Based Access Control Reinvents Security
Google to display only interest-based ads using a privacy sandbox
Ethical Considerations in Digital Banking: Privacy, Data Ethics, and Responsible AI
How to Check if an Android App is Safe to Download?