A virtual hard disk is a virtualization technology, that allows us to create and use a disk drive that is physically not present as hardware on the PC or server system. VHDs can be formatted and used in two types of file systems NTFS or exFAT on Windows 10 or earlier.
Just the like virtual memory, the speed of virtual drives are much faster than other physical hard disk attached to the same machine. Therefore, if you have big size HDD, virtualizing one or more hard disks can speed up the data moving or copying within the disk, thereby increasing the operating speed. Although the VHD is physically not present, yet it consumes the hard drive space on which it has been created.
We can store files and folders on VHD just like any other drive, but where all this data will go? Actually, a virtual hard disk is saved on the system as a file. If you have ever used VirtualBox, you already have used VHDs. All its operating system can best install on VHD (virtual Hard disks) that resides on the physical HDD in a single file format with .vhd extension.
We can use Virtual Hard disks in two types of file systems that allow by the Windows to format it. While creating a VHD on Windows 10 or 7, you will get an option to format the drive in NTFS or exFAT. Just like any other Physical HDD.
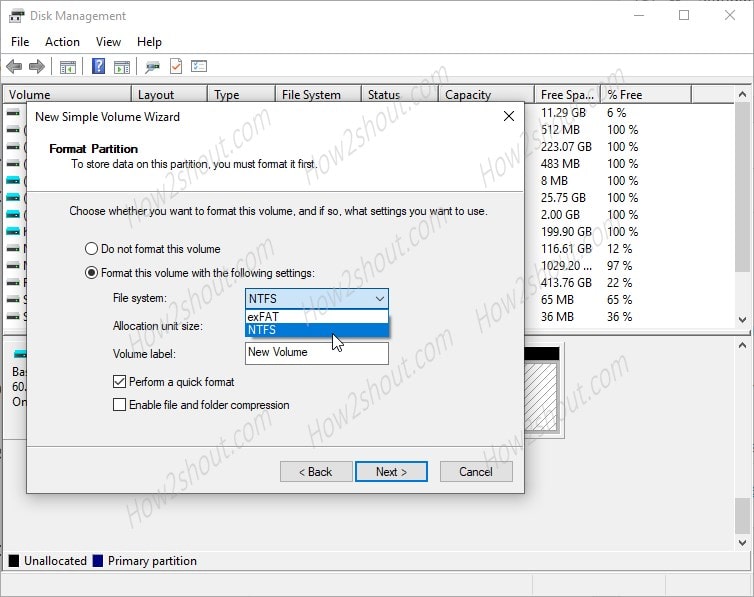
NTFS stands for “New Technology File system” developed by Microsoft to use in its Windows NT Kernel series of operating systems and since then it has been used continuously. Before that FAT was there. The benefits of it are, it provides data protection features and easy recovery because apart from writing data, NTFS also keeps logs of all changes; we can also use long file names on this file system format.
The NTFS file system has three functions: error warning function, disk self-repair function, and log function.
Error warning function: If the disk sector where the MFT (Master File Table) that store all information of files and folder saved on the disk located somehow gets damaged; the NTFS file system will intelligently change the MFT to other sectors of the hard disk to ensure the normal function of the file system and other operations. Whereas the older FAT16 and FAT32 FAT if the sector is damaged, the entire file system will be paralyzed.
Disk self-repair function: NTFS can automatically detect and repair logical errors and physical errors on the hard disk. It checks the sector every time, we write or read data on it whether the sector is correct or not. When an error is found while reading, NTFS will report the error however while writing, something like that happens it will jump to an intact sector of the drive to store the data.
Log function: In the NTFS file system, any operation can be regarded as an “event”. The event log has been supervising the entire operation. When it finds the complete file at the target location, it will be marked as “completed”. This makes recovery of the file system better.
On the other hand exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table File System, extended FAT) also developed by Microsoft and generally used for Flash or USB drives for Windows Embedded 5.0 and above (including Windows CE 5.0, 6.0, Windows Mobile5, 6, 6.1).
The reason behind developing this was NTFS is not suitable for flash drives while FAT32 has a limitation of not supporting drives more than 4GB in size. Therefore, we can say exFat is something between FAT32 and NTFS in terms of extra features but not in data storage value as compared to NTFS. Another reason why exFat is not suitable for HDD or VHD is it doesn’t provide a journaling file system and other features mentioned above while we were talking about NTFS.
Therefore, as we are using the Virtual Hard Disk on the Windows system as Physical hard disks, thus it would be a sagacious decision if we go for NTFS file system format.
Related Posts
How to enable Virtualbox nested VTX/Amd-V on Windows 10/11 or Linux
How to Install Sandbox in Windows 11 or 10 Home Editions
How to install Redhat Podman on Windows 10 or 11 via CMD
Install Docker Desktop on Windows 11 or 10 via PowerShell
How to Install Minikube on Windows 11 or 10 using CMD or PowerShell
High to Low-end Android Emulators to Try on Mac and PCs in 2023