Learn a simple way to manually install CentOS on Windows 10 Subsystem for Linux in order to run RHEL’s RPM or YUM repository commands…
Windows Subsystem for Linux is a state-of-art feature for users. Since it lets you practise and learn Linux operating system commands directly on Windows 10 system without any usage of virtual machines software like VirtualBox. Windows Subsystem for Linux which is also called as WSL, in short, a layer implemented by Microsoft in Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019 operating systems for providing compatibility and execution of Linux binary executables natively.
To install a Linux Distro image generally we depend on Microsoft store, where a couple of pre-compiled lightweight images are present. Currently, available Linux WSL images are Ubuntu, Kali Linux, Debian, AlpinLinux, OpenSUSE and SUSE Enterprise Server. Thus, if you want to try some Linux OS such as CentOS/RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise) and Arch Linux then we have to manually install them on Windows 10 Subsystem for Linux. Here we will show how to do that?
How to install CentOS 7 on Windows subsystem for Linux
Note: Before installing CentOS on WSL, you must have enabled Windows subsystem for Linux. If you don’t know how to do that then read this: Enable WSL on Windows 10
1: Download CentOS WSL
The first thing we need a CentOS on WSL (Windows 10 FCU or later) based on WSldl. Basically, it is a zipped file that contains rootfs and other files. The CentOS as a WSL Instance is an open-source project available on Github, so get it from here. The latest version CentOS it offers is CentOS 7.6.
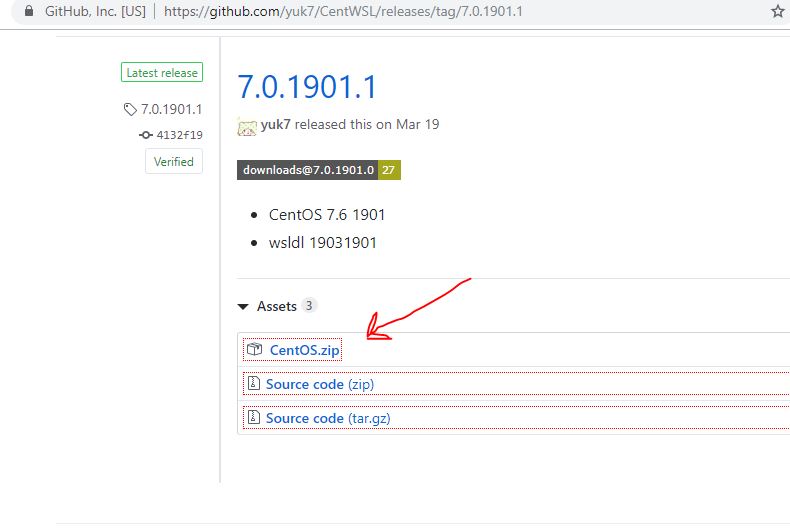
2: Unzip WSL CentOS 7.x zipped folder
The size of the downloaded folder would be around 300MB and after downloading right click and unzip the folder. Here we are using WinRAR to extract the files, however, you can use Windows default or any other program to unzip it.
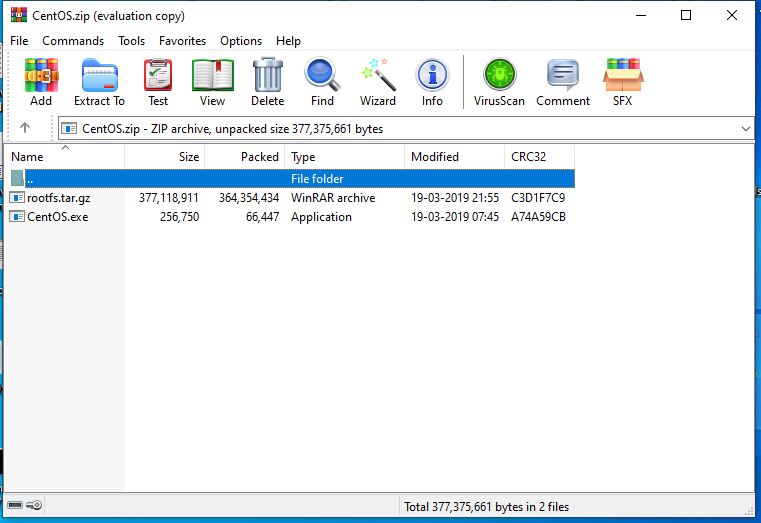
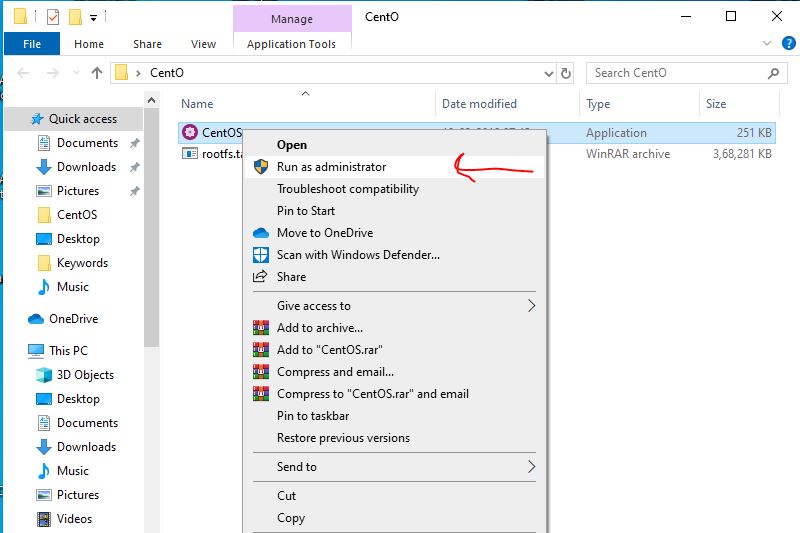
3: Run CentOS.exe to install it on Windows 10 subsystem for Linux
After extracting the folder, inside it you will see two files one is rootfs.tar.gz and second one is CentOS.exe. We need to run CentOS.exe in order to extract the files and registering them on WSL. Rightclick and run as Administrator.
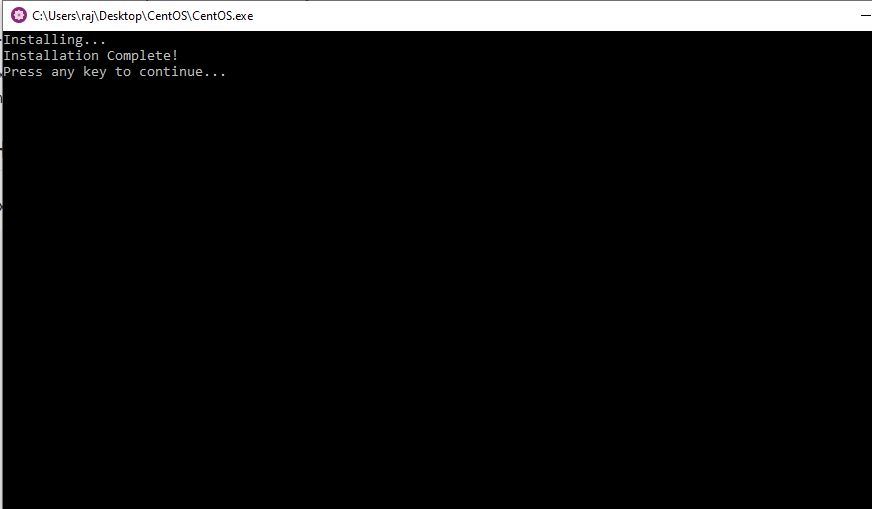
4: Installation complete
Once the installation is complete, you will get a message for that on the CentOS command screen. Now press Enter key to exit the setup.
5: Run CentOS 7 on WSL
To run it, again go to the extracted folder of the centos for WSL and this time you will see four files. Out of them again right-click on Centos.exe and run as administrator.
Finally, our manually installed Linux subsystem for CentOS is here.
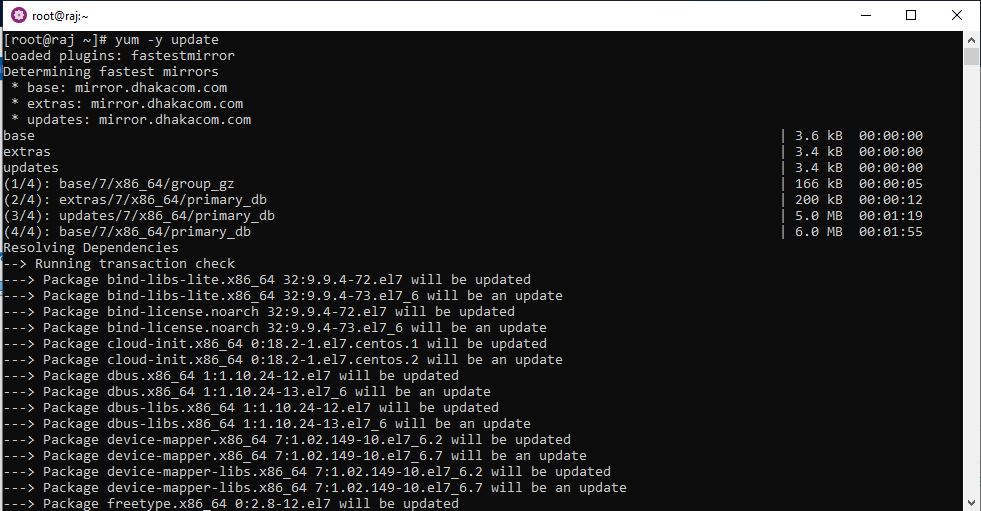
6: Command to update Centos on WSL
You can run any command which would like to execute on CentOS, however, just for checking whether it is working fine or not we are running CentOS update command using YUM.
yum -y update
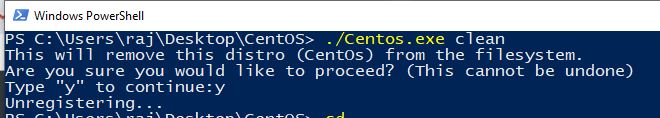
7: Uninstall CentOS 7 WSL
To uninstall it, run PowerShell as admin switch to CentOS directory and just use the below single command:
./CentOS.exe clean
Some other information to combat, if you get any error while running it.
If in the future you have accidentally deleted the CentOS WSL folder and want to reinstall it then first we need to clean the existing installation.
For that first of all again extract the files from the CentOS zipped folder that we have downloaded above and then run Windows 10 PowerShell an administrator, navigate to the extracted folder, and again run the below command:
./CentOS.exe clean
To reinstall again run the same CentOS.exe present in the same extracted to register files to WSL- Windows 10 subsystem for Linux.






Hello, thank you. But how to use Centos on WSL? SystemD is not working here? Is there some trick? Thank.
In the article you can see the way to use CentOS on WSL -Windows subsystem for Linux, however, you can’t use SystemD yet because Centos or other Linux distro on WSL1 do not boot with SystemD or init.
This post provides clear idea for the new viewers of blogging, that genuinely how to do
blogging.
H2S Media Team ,
I am getting this error here :
ERROR: LoadLibraryEx() failed to load wslapi.dll
Press any key to exit…
Please check your Windows version is Windows 10 version 1709 (16251) 64bit or later only and also make sure WSL is enabled.
How can i install apache, PHP AND MYSQL on this WSL system ?
I had already installed PHP and composer natively on Windows 10, but I believe the WSL will not see those and would need its own php installation ?
Yes, Indeed, we need to install PHP on WSL separately. Standard or naive installation on Windows 10 will not work for Linux instances.
I let Windows Defender scan the two files which are included in the zip. Windows Defender thinks that it found the Trojan Win64/Longage in the files usr/bin/dbus-daemon and usr/bin/systemctl. I won’t install until I know that this is a false positive.
It’s a false positive. Microsoft eventually removed the detection. See: https://askubuntu.com/questions/1194796/windows-defender-reports-win64-longage-trojan-malware-in-ubuntu-18-04-3-live-ser
Suggestions as to the best resource to install and support Postrgres on this Centos on WSL2?
The installation of Postgres on CentOS over WSL will be the same as we do on regular CentOS Desktop OS. Whereas after that if you want to learn further about it then postgresqltutorial.com could help.
How to run it later as a non-Administrator? Like the ones installed from the Microsoft Store
Of course, you can. Instead of running it as Administrator simply double click on the setup and it will run as non-administrator
This installation works great. However it seems the bash shell is ignoring LS_COLOR settings in the terminal console. Any direction on how to get color in the directory listings?
Simply run this command-
alias ls='ls --color=auto'And let me whether it worked in your case or not…
Is it possible to install a 2nd fresh CentOS 7 WSL instance?
No, for that you have to remove the previous one. However, you can install the CentOS8 WSL version. Then you will have two different CentOS versions on the same system.
Installation directory not found: C:UsersMemSQLAppDataLocalTempRar$EXa18276.36451CU
What will be the reason?
or how i can redirect to another directory
This is great, and it’s working well for me, except that I was wondering if there is any way to tell CentOS7 to immediately claim X amount of RAM from Windows for Linux as a huge chunk and limit its use to that and only that, so it’s never having to involve Windows’ memory manager once running?
For example, I have 64GB of RAM, that I’d like to give half of to Linux to manage completely on its own, never having to go to Windows memory manager after CentOS7 is launched.
Awesome Documentation! Thank you!