Manage your system logs with a web interface by installing open source Graylog log management platform on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Linux. To help you with that, here is the step-by-step tutorial.
Open source software(s) are the backbone of modern society computers because most of the commercial servers run on Linux operating systems. Under this category, we also have a variety of application platforms to solve the various problems of organizations and individual users, for example, the one which we are going to discuss here in this article i.e. “Graylog“.
As the name of this software suggests, it is meant to do something with system logs. Yes, it is for collecting, indexing, and analyzing log data from various sources, and all this in real time. So, if you are a system administrator handling a network of servers, desktops, and other devices, then using the Graylog you will have a centralized place for monitoring system logs, application logs, or network logs. This logging system essentially consists of the web interface, the Graylog servers, the Elasticsearch nodes, and a Mongo database.
Graylog supports various input mechanisms. By default, four different formats or protocols are supported: Syslog, GELF, JSON / REST-URLs, and RAW. syslog is a standard for the transmission of log messages and is often used by system components.
Prerequisites: To get Graylog installed on our Ubuntu 22.04 system we need:
- A server or virtual machine running Ubuntu .04 or later.
- MongoDB andElasticSearch
- At least a non-root user with
sudorights - Ubuntu server with 4 CPU Cores and 8 GB RAM
Graylog on Ubuntu 22.04 Installation Steps
1. Update and Install dependencies
Start with the system update command first on your Ubuntu terminal, so that the already installed packages can be updated.
sudo apt updateApart from updating the system, we also need a couple of packages to ensure the proper installation of Graylog.
sudo apt install apt-transport-https wget curl uuid-runtime ca-certificates gnupg22. Installing MongoDB 6.x on Ubuntu 22.04
Ubuntu 22.04 Linux doesn’t offer the latest packages to install MongoDB from its official repository, hence we have to add an extra repo manually.
While writing this article, the latest version of the MongoDB was “7.x“, however, GrayLog only supports up to Mongodb 6.x. Hence, we are installing that. In your case, if it is different then change the version number – 6.0 in the given commands with the one that you want to install:
curl -sSL https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-6.0.asc -o mongoserver.ascgpg --no-default-keyring --keyring ./mongo_key_temp.gpg --import ./mongoserver.ascgpg --no-default-keyring --keyring ./mongo_key_temp.gpg --export > ./mongoserver_key.gpgsudo mv mongoserver_key.gpg /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/Add MongoDB Repository:
echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs)/mongodb-org/6.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-6.0.list Run the System Update:
Let the system know about your newly added repository by running the system update command:
sudo apt updateGraylog uses MongoDB to store data, hence now we can install it on our server so that later the generated logs can be saved there for further analysis.
sudo apt install mongodb-orgEnable and start the Database Server services:
sudo systemctl enable --now mongodsudo systemctl restart mongod.serviceTo check whether it is running properly without any errors you can run:
sudo systemctl status mongod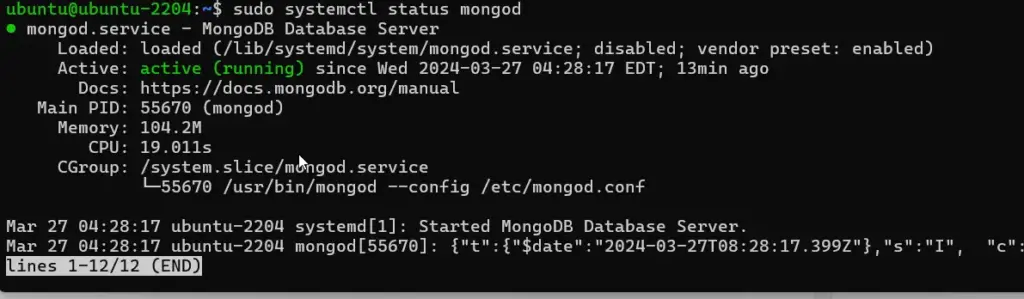
3. Setting up ElasticSearch
The next thing we need to install to set up Greylog is Elasticsearch or OpenSearch, here we are using the EalsticSearch community version which is a full-text search and analytics engine. As greylog can handle logs from multiple sources, hence it needs a platform that is highly scalable and allows users to store, search, and analyze big volumes of data quickly and in near real-time.
Note: The only supported version by Graylog of Elasticsearch is 7.x.
Add GPG Key:
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpgAdd Elastic Search repository:
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg] https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.listCommand to Install ElasticSearch open-source version on Ubuntu 22.04:
sudo apt update && sudo apt-get install elasticsearch-ossModify the Elasticsearch configuration file to set the cluster name to graylog and add action.auto_create_index: false
For this simply copy-paste the below given command block and hit the Enter key.
sudo tee -a /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml > /dev/null <<EOT
cluster.name: graylog
action.auto_create_index: false
EOTEnable and start Elastic search service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable --now elasticsearch
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
#### To check service status:
sudo systemctl status elasticsearch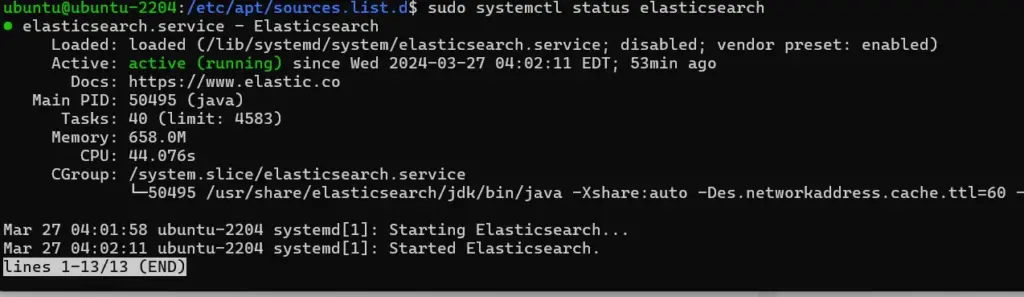
4. Install Graylog Server on Ubuntu 22.04
Download the repository of Graylog that is available as a deb package. The version of Gralog while doing this article was 5.0.
wget https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-5.0-repository_latest.debInstall it:
sudo dpkg -i graylog-5.0-repository_latest.deb
Now, update your system, so that it can recognize the newly added repository to download the packages for Graylog:
sudo apt updateFinally, install it
sudo apt update && sudo apt-get install graylog-serverExtra: If you also want to install the Integrations Plugins or the Enterprise Plugins, then run:
sudo apt install graylog-enterprise-plugins graylog-integrations-plugins graylog-enterprise-integrations-plugins5. Edit the Graylog configuration file to set the admin Password
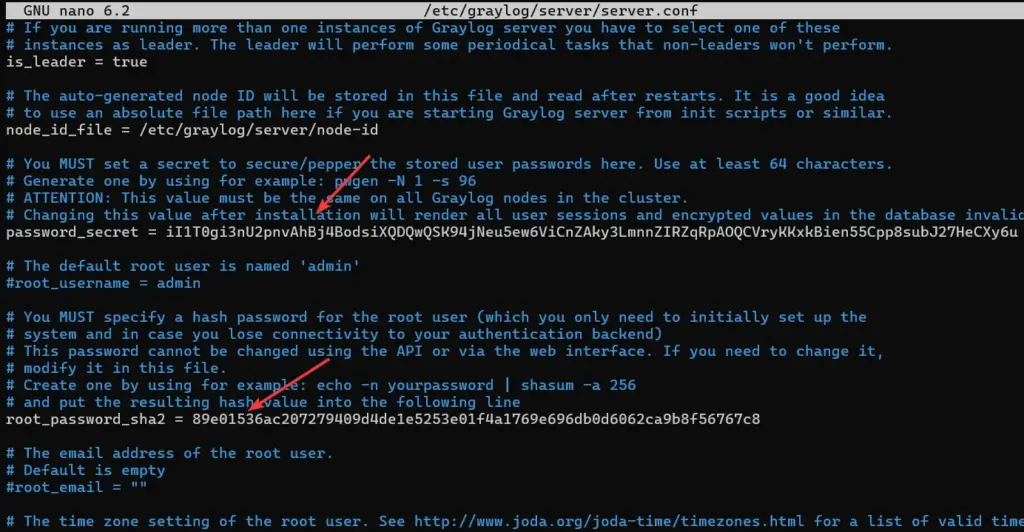
There are two password values- password_secret and root_password_sha2, we need to configure them otherwise Graylog on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS will not start at all.
These two values are present in the Graylog configuration file and what we set for them will be used to secure user passwords and log in to the admin user on its web interface. But we cannot set a plain text value for them instead we have to generate a hash. So, run:
Set password_secret key
< /dev/urandom tr -dc A-Z-a-z-0-9 | head -c${1:-96};echo;The above command will generate a secret key to secure user passwords, so copy that and edit the configuration file using:
sudo nano /etc/graylog/server/server.confNow, find password_secret = in the file and paste the copied secret key in front of it. As shown in the below screenshot.
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X, Y, and hit the Enter key.
Set root_password_sha2 hash
The default username to log in Graylog web interface is admin, whereas the password needs to be set, that’s what we are doing here. Generate a hash for the password you want to set using the below-given command:
echo -n "Enter Password: " && head -1 </dev/stdin | tr -d '\n' | sha256sum | cut -d" " -f1When the system asks you to Enter the password type whatever you want to use and you will have the hash string to paste in the Graylog configuration file.
As you hit the Enter key after using the above command, a hash sum will be generated. Copy it.
Now, again edit the configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/graylog/server/server.confFind the line: root_password_sha2 and paste the hash sum in front of it, as shown in the below screenshot:
Also, by default, the Graylog is only accessible using localhost IP i.e. 127.0.0.1 thus in case you are planning to access its web interface remotely, then change it with your server IP address in the configuration file.
Find the line: http_bind_address, uncomment it and change 127.0.0.1 with the IP address of your system where you are installing graylog.
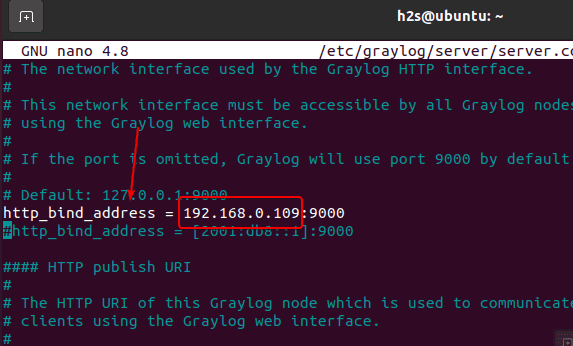
Save the file– Ctrl + X, Y and hit the Enter key.
6. Enable and Restart the Graylog Server
We already have done all the essential configurations, and now enable this log system service to start automatically.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable --now graylog-server
sudo systemctl restart graylog-serverCheck whether it is running without any error or not:
sudo systemctl status graylog-server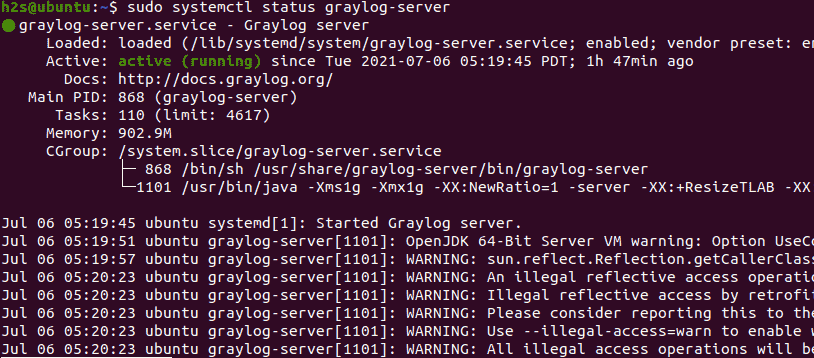
If you are planning to access the Graylog web interface remotely then also open port 9000 in the Ubuntu firewall:
sudo ufw allow 90007. Access the Web interface
Open a browser on your local system or remote that can access the Ubuntu 22.04 server IP address. And type the http://your-server-ipaddress:9000
Replace your-server-ip-address with the actual IP address of your Server where Graylog has been installed.
The default username is admin whereas the password is what you have set in step 5 of this article for root_password.
8. Example: Send Sys logs of the host system to Graylog
Let’s test our Graylog instance by sending the server logs where it has been installed.
Create a config file under /etc/rsyslog.d/ to tell the system where to send the logs.
sudo nano /etc/rsyslog.d/graylog.confAdd the following line:
For UDP:
*.* @your-server-ip:5140;RSYSLOG_SyslogProtocol23FormatIf you want the TCP to send logs then add two @@ instead one in the above command:
*.*@@172.16.10.51:5140;RSYSLOG_SyslogProtocol23FormatReplace the your-server-IP with the IP address of the system from where you are sending the logs. If it is a host system where you have installed the Graylog then use the IP address of that.
Save the file by typing Ctrl+X, Y, and hit the Enter key.
Restart Syslog on the server from where you want to send logs, here we are sending the logd of the host server:
sudo systemctl restart rsyslogNow, add Input for Node in Graylog.
On the Dashboard of Graylog click on the System -> Inputs.
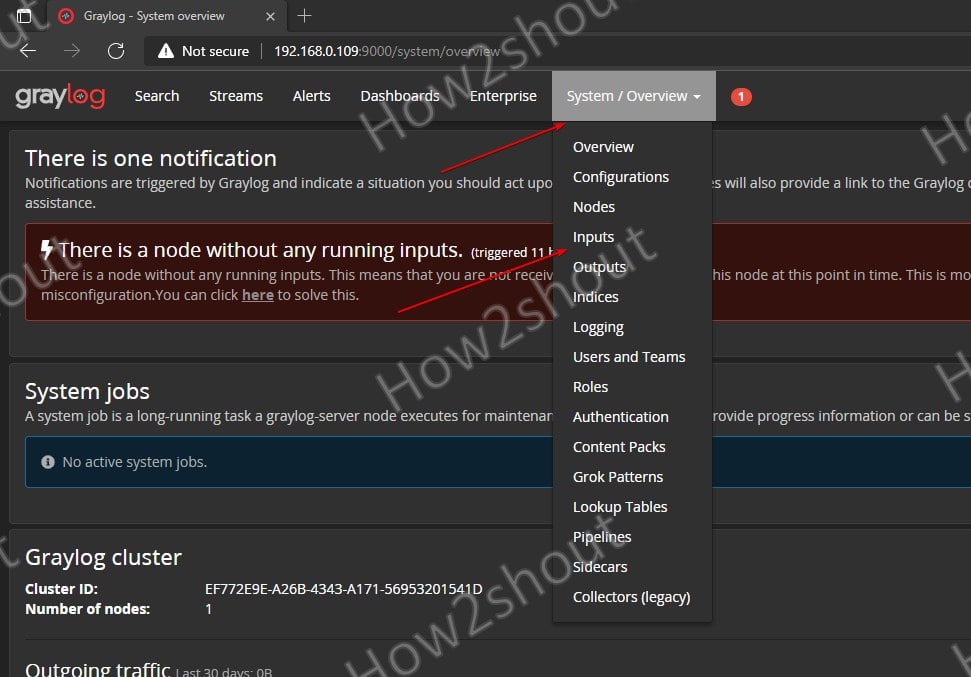
Select Syslog UDP and hit the Launch new input button.
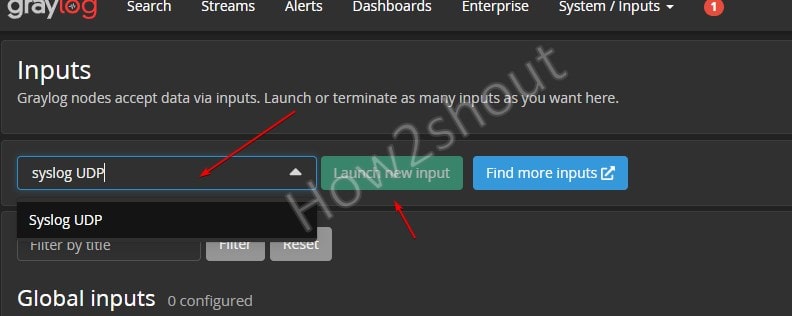
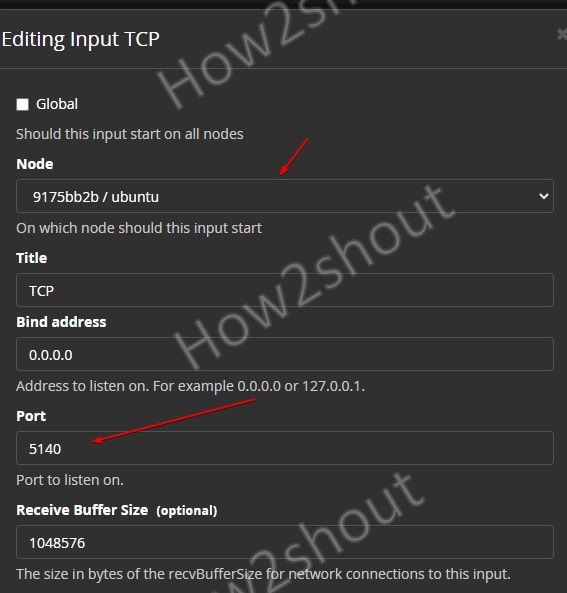
Select the node from the drop-down box, give some title (whatever you want) to Input, and then set the port number to 5140 after that scroll down and save the configuration.
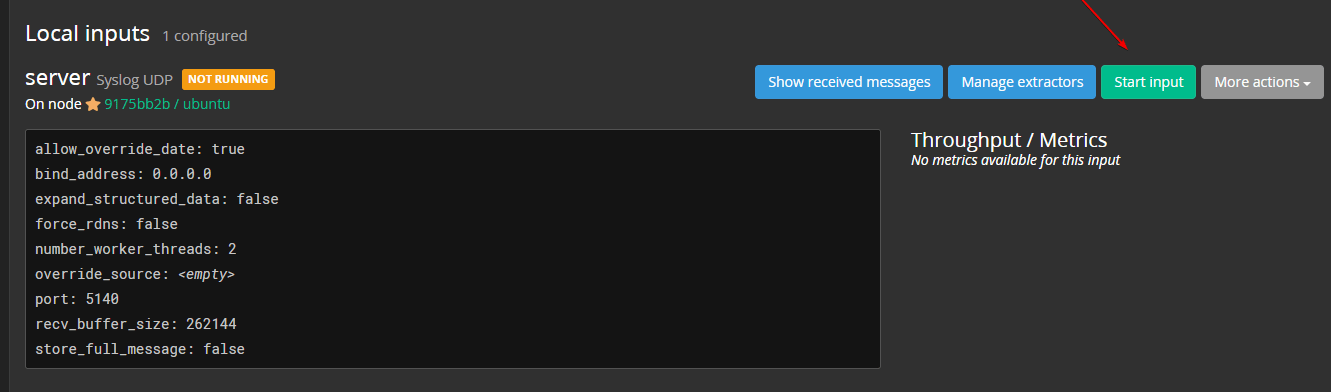
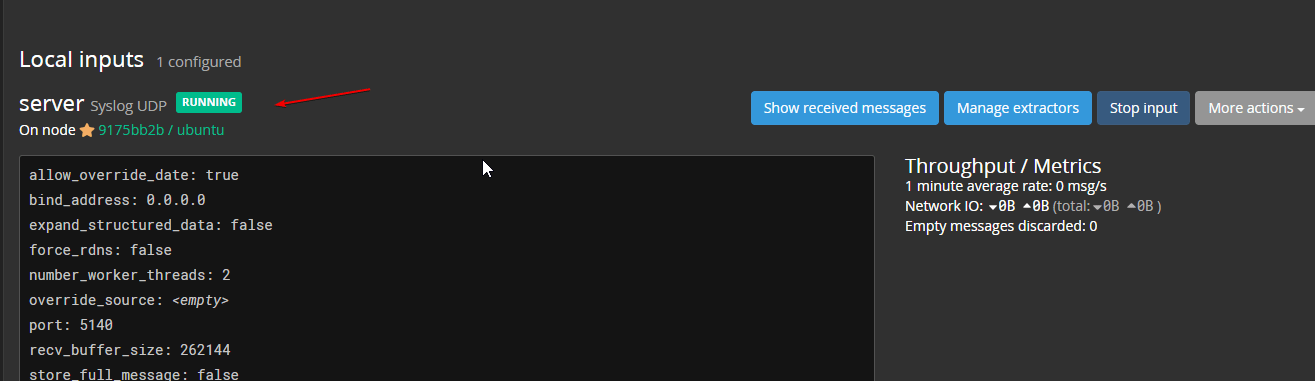
Now, click on the “Start Input” button to start the server input.
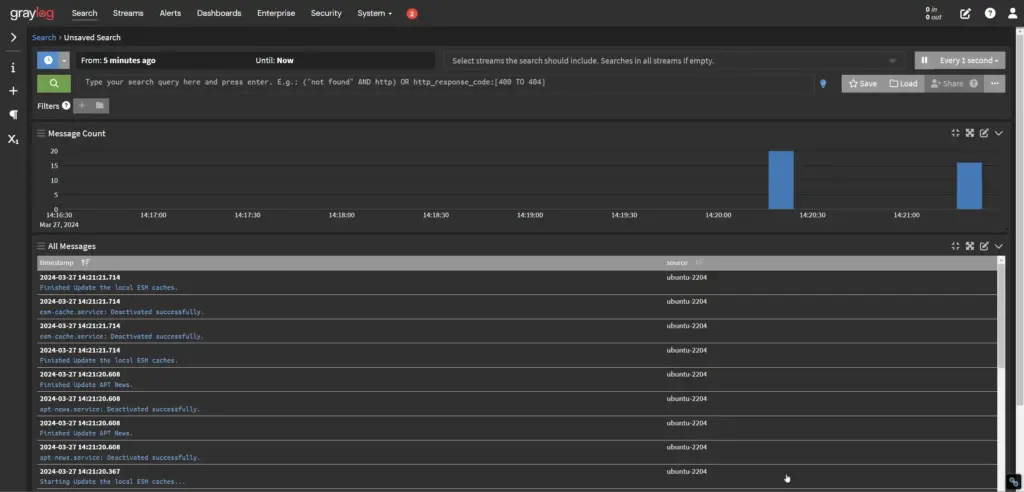
9. Metrics Dashboard
Once the Input from the server starts, click on the Search given in the Graylog menu and you will start getting metrics and logs in real-time from your server. Also, you can set the frequency of metrics updates.
To know more about this log management tool and other configuration tasks refer to official documentation where you will also find the way to use Nginx/Apache as a reverse proxy and HTTPS in Graylog.